Table of Contents
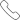
Booster compressors are critical components in various industrial applications requiring high-pressure gas systems. These devices are specifically designed to increase the pressure of gases to levels necessary for a wide range of processes, including in power plants, chemical industries and natural gas facilities. Air booster compressors are integral in maintaining consistent gas pressure for optimal system performance.
However, it operates under high-pressure conditions, which inherently introduces certain risks. Proper safety protocols are essential to ensure safe operation, prevent accidents and extend the lifespan of the equipment. This article outlines the key safety guidelines for operating booster compressors in high-pressure applications, with a focus on best practices, preventive maintenance and emergency preparedness.

Understand the Basics of Gas Boosters and Their Operation
Importance of Knowledge:
Before operating a booster gas compressor, it’s crucial to understand how the system works. Gas boosters increase the pressure of incoming gases by utilizing compression technology, often powered by air or mechanical energy. Booster compressors are typically activated when the incoming pressure falls below a required threshold, ensuring that the desired pressure is maintained for continuous operations.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Having a clear understanding of the working principle of booster compressors helps operators identify potential hazards and take appropriate action in case of malfunction. For example, a sudden drop in pressure could indicate an issue with the compressor or the system, which needs immediate attention to avoid risks such as over-pressurization or system failure.
Follow Guidelines for Installation and Operation
Adhere to Manufacturer’s Specifications:
Each booster compressor comes with a set of guidelines from the manufacturer, which includes recommended installation, operation and maintenance procedures. These guidelines are tailored to ensure that the system operates within safe limits, providing clear instructions on pressure settings, temperature ranges and suitable materials for use.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Deviating from these specifications could lead to overloading the booster gas compressor, risking damage or failure. Properly following the installation instructions ensure that the system is set up correctly, minimizing the risk of mechanical failures or hazardous conditions.
Safety Tip:
- Always verify that the compressor is compatible with the specific gas or medium being handled.
- Ensure that the system is installed in an environment that meets all required safety standards and specifications provided by the manufacturer.
Regularly Monitor and Maintain Pressure Levels
Pressure Management:
In booster compressors, maintaining a consistent and safe operating pressure is one of the most important safety considerations. Gas boosters are often used in high-pressure environments, which mean that if the system’s pressure is not carefully monitored and controlled, the risks of over-pressurization and failure increase.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Over-pressurization can cause critical damage to the air booster compressor and surrounding equipment, resulting in explosions or gas leaks. On the other hand, insufficient pressure may lead to operational inefficiencies and incomplete processes.
Safety Tip:
- Install Pressure Gauges: Ensure that pressure gauges are installed at key points in the system to allow operators to continuously monitor pressure levels.
- Pressure Relief Valves: Implement pressure relief valves to release excess pressure if it exceeds preset limits, preventing catastrophic system failures.
- Routine Monitoring: Continuously monitor pressure during operation. Use automated systems with built-in alarms to notify operators of any pressure anomalies.
Proper Ventilation and Cooling
Ensure Proper Cooling:
Booster compressors, especially those operating in high-pressure systems, generate significant amounts of heat. Overheating can result in system failures or even fires, especially in systems where flammable gases are involved.
Why It Matters for Safety:
If an air compressor overheats, it can lead to system malfunction, excessive wear or even combustion. Adequate cooling ensures that the compressor operates within its designed thermal limits, preventing overheating.
Safety Tip:
- Proper Ventilation: Install the booster compressor in a well-ventilated area to allow heat to dissipate.
- Check Cooling Systems: Ensure that the cooling mechanisms – whether air- or liquid-cooled – are functioning properly. Regularly clean cooling fans, filters and radiators to ensure efficient heat dissipation.
- Use Temperature Sensors: Install temperature sensors to monitor the internal temperature of the compressor and the surrounding environment.
Gas Handling Protocols
Proper Gas Selection:
Different gas boosters are designed for specific gases, such as natural gas, air, nitrogen or inert gases. Using the wrong gas or mixing gases improperly can result in dangerous reactions or equipment failures.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Each type of gas has its unique characteristics and handling requirements. Incompatible gases could lead to system failure, toxic gas emissions or explosions.
Safety Tip:
- Check Compatibility: Before using a vacuum booster compressor, confirm that it is rated for the type of gas you intend to compress.
- Proper Gas Storage: Ensure that gases are stored in appropriate cylinders and that the equipment is properly labeled to prevent incorrect gas usage.
- Safety Valves and Monitoring: Use safety valves and gas detection systems to ensure that only the correct gases are being used and that any leaks or exposure are immediately detected.
Emergency Shutdown and Safety Features
Establish Emergency Procedures:
In high-pressure applications, emergency situations can arise due to system malfunction or external factors. It is critical to have emergency protocols in place to quickly address issues like gas leaks, pressure malfunctions or system failures.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Effective emergency response can mitigate the damage caused by system failures and protect personnel and equipment from catastrophic harm.
Safety Tip:
- Emergency Shutdown System: Implement an emergency shutdown system that can be quickly activated to stop gas flow in the event of an emergency.
- Training: Ensure that all personnel are properly trained on emergency procedures, including how to shut down the system and evacuate the area if necessary.
- Safety Equipment: Equip workers with PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) such as gloves, goggles and protective clothing to prevent injuries during emergencies.
Implement Regular Safety Training and Drills
Training for Operators:
Safety protocols and emergency procedures should be communicated to all personnel working with or around the compressor. Regular safety training ensures that everyone knows what to do in case of an emergency and it prepares them for unexpected situations that may arise.
Why It Matters for Safety:
Adequately trained personnel are more likely to follow safety procedures and react quickly to prevent accidents, leading to safer operations and fewer injuries.
Safety Tip:
- Conduct Regular Drills: Regularly conduct safety drills to practice emergency shutdown procedures and other key actions.
- Operator Certification: Ensure that operators are certified and well-versed in compressor booster safety operations and maintenance protocols.
Conclusion
Operating booster gas compressors in high-pressure applications requires a keen understanding of the system’s components, safe operation practices and preventive maintenance strategies. By adhering to manufacturer guidelines, regularly monitoring pressure levels, ensuring proper ventilation and following gas handling protocols, operators can ensure that gas boosters perform optimally while minimizing risks.
Safety should always be a top priority and implementing the right safety measures – such as proper training, emergency protocols and ongoing inspections – will help mitigate hazards, reduce downtime and protect both personnel and equipment. By following these safety guidelines, industries can ensure the safe and efficient operation of booster compressors in high-pressure environments.
FAQs about Operating Booster Compressor
What is a booster compressor?
A booster compressor is a device used to increase the pressure of a gas to required levels for industrial applications, ensuring consistent pressure and smooth operation in various processes.
What should I do if the pressure in the booster compressor exceeds safe limits?
If the pressure exceeds safe limits, activate the pressure relief valve and shut down the compressor immediately. Ensure that the emergency shutdown system is functioning properly to avoid over-pressurization and damage.
What are the key safety measures for operating a gas booster compressor?
Key safety measures include following manufacturer guidelines, monitoring pressure levels, maintaining proper ventilation, ensuring the compressor is compatible with the gas being used and training personnel on emergency procedures.
Why is proper ventilation important when operating a gas booster compressor?
Proper ventilation helps dissipate heat generated during operation, preventing overheating and ensuring the compressor operates within safe temperature limits, thereby reducing the risk of failure and accidents.
About Author

CEO
Mr. Vishwesh Pardeshi is the CEO of Acme Air Equipments Company Pvt. Ltd., an industrial and engineering goods manufacturing company based in Ahmedabad, Gujarat (India). He has taken over the responsibility from founding Partners and Directors of the Company, and is now leading a talented group of professionals since 2020 by bringing in vast industrial and management expertise. By qualification, he holds a Bachelor Degree in Mechanical Engineering and also holds a MBA degree from reputed institutes. Under his leadership, the Company has successfully executed prestigious projects by delivering high quality and world class products from a state of the art manufacturing facility which combines CNC-enabled precision manufacturing and strong after sales support. In line with the Vision, Mission and Core Values of the Organization, Mr. Vishwesh Pardeshi continues to drive Quality, Reliability and Global Expansion at Acme Air Equipments Co. Pvt. Ltd.